Role
UX Professional (Team Lead)
Company
Codesplice
Type
SaaS Product
Time
11 months
My Part
Developed an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system, established a robust UI design system, process flows and delivered within scope, timeline and budget constraints.
Conducted user research and competitive analysis for ERP platforms, working with OrderWise.
Led the digitalization of stock management processes, streamlining inventory control and operational efficiency.
Facilitated on-site client discussions in the Czech Republic, gathered user stories, presented designs, iterated, and coordinated with cross-functional teams internationally, stakeholders, developers, and testers.
Challenge
The goal of this case study is to outline the UX design process for creating a SaaS ERP system tailored for pharmaceutical industries.
Solution
The ERP system aims to streamline operations, ensure compliance with industry regulations, and enhance efficiency for pharmaceutical companies.
01
Research
02
Define and Ideate
03
Design and test
User research
Conducted interviews and surveys with pharmaceutical industry professionals to understand their workflows, pain points, and needs related to ERP systems.
Identified key user personas representing roles such as manufacturing managers, quality assurance specialists, warehouse staff, and IT administrators.
Competitive analysis
Analyzed existing ERP systems and software solutions catering to pharmaceutical industries by assessing their features, functionalities, user interfaces, and pricing models.
Studied industry regulations, compliance standards, and best practices.
Identified gaps and areas for improvement compared to existing solutions.
Persona
Understanding process on-site
Warehouse
Users maintain Goods-IN and Goods-OUT book to record stock and their specifications.

Data protection
ERP systems are generic. Users cannot specify which users will have access to which suppliers and customers.

Reports
Reports generated by the system is not in compliance with the authorities. The format varies with different countries.

Excel Sheets
Users maintain an excel to record Purchase and Sales activity to track product life-cycle and annual valuations. It is approximate as it is not possible for them to update the excel all the time.

key Insights
confidentiality
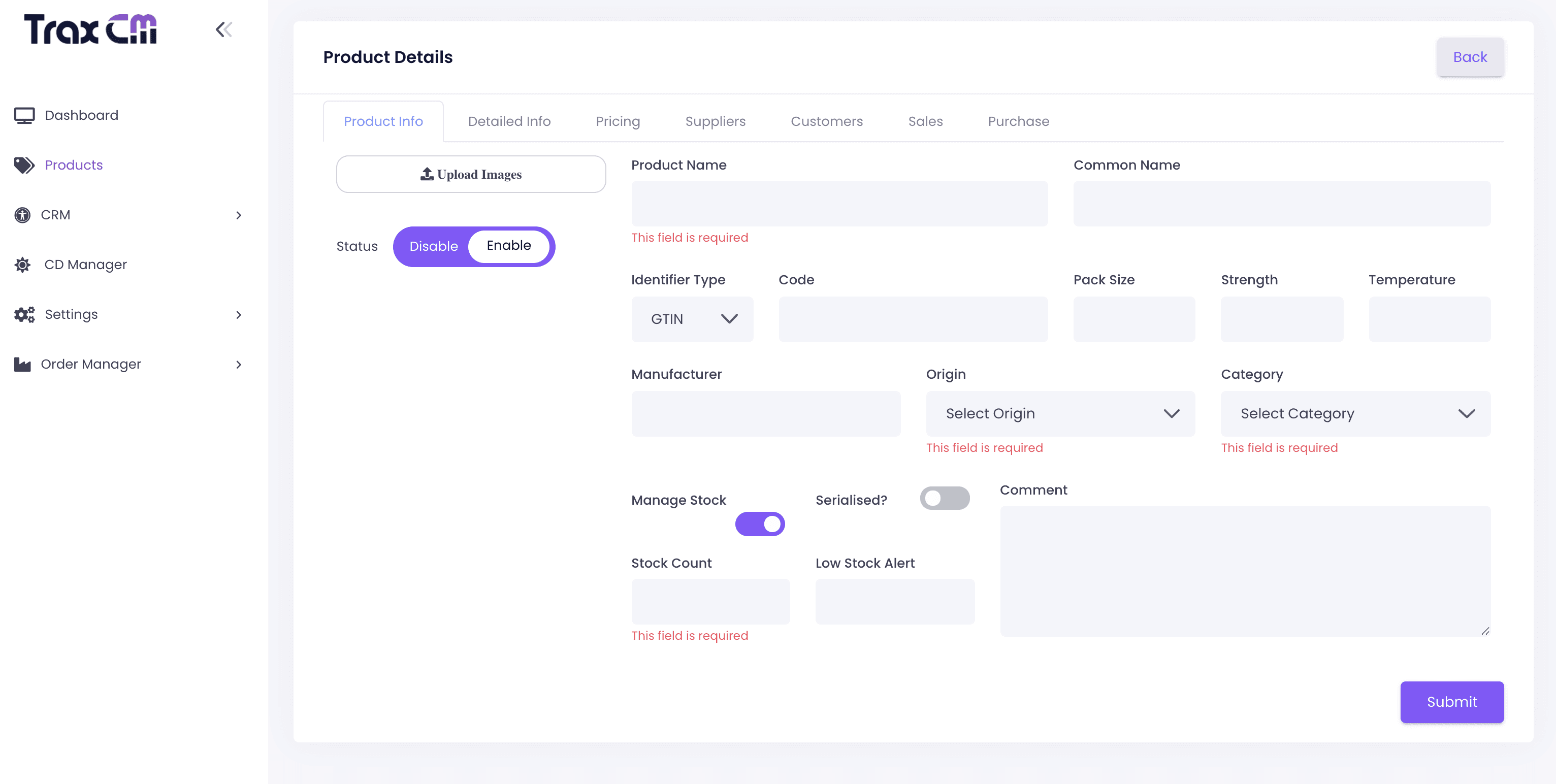
Role-based access permissions restrict access to sensitive data and implement data encryption, and user authentication.
Regulatory and compliance
System should be pharma inclined, and compliant with regulations of different authorities in different countries.
tracking and reports
Standard and customizable dashboards and reports allow users to generate and analyze data.
How manual process can be digitalized?
IN and OUT book
A setup can be designed to record stock activity coming and going from the warehouse.
product lifecycle
Dashboards can be designed to showcase product data and transaction trace.
Discrepencies
Instead of manual notes, a separate section for comments can be provided which will be forwarded to the next team for further action.
reverse flow?
Returns and recalls
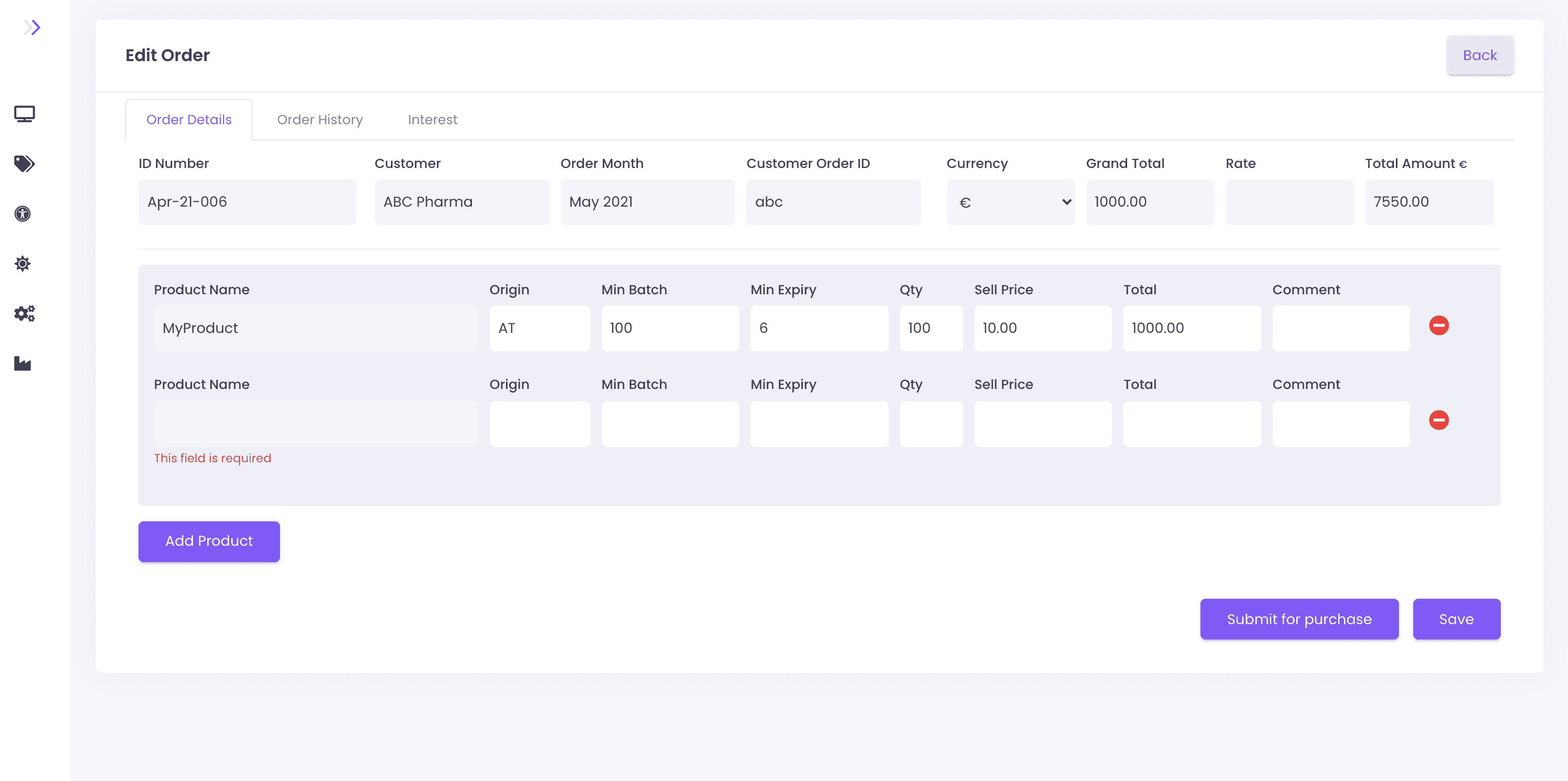
Purchase Orders and Sales Orders should be capable of undoing the calculations in the system whenever there is recall or return.
Credit and debit note
Raising credit and debit notes should re-calculate the stock and margin valuations and user should be able to track the activity.
order cancellation
User should track the cancellations and therefore updates supplier and customer history.
My monster charts
Whoops!
I dug too deep! :(
I got lost in the loop. I started getting into deeper scenerios and loosing the grip over the track. I got too many information about too many areas and I started making up flows for different modules at the same time.
Peers to the rescue! :)
My peers helped me to get out of the loop.
I realised I have to start with the high level overview instead of deeper scenerios.
Once the modules are finalized, I can start digging up scenerios one module at a time.
Here
We
Go!
One step at a time
User Journey
Prototypes
The prototype outlines the navigation structure of the ERP system, including menus, sub-menus, and navigation paths between different modules and features.
It illustrates how users can move through the system to access various functions and data.
Usability Testing
Conducted usability testing sessions with end-users to evaluate the effectiveness of the design.
Identified usability issues, pain points, and areas for improvement.
Gathered qualitative and quantitative data to inform design decisions.
Demonstration and Walkthrough
Demonstrated ERP system, guiding users through the various modules, screens, and interactions.
Highlighted key features and functionalities, demonstrating how users can perform common tasks and achieve their goals within the system.
Iteration
Iteratively refined the design based on user feedback and testing insights.
Enhanced the interface to improve usability, accessibility, and overall user experience.
Ensured consistency across different devices and screen sizes.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) System
Control Drug (CD) Management
Order Management
Product Management
Conclusion
The ERP SaaS product represents a significant step forward in the digital transformation of the pharmaceutical industry. By focusing on user needs, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring compliance, the system not only supports operational success but also empowers pharmaceutical industries to drive better business outcomes.
Launching soon